Beyond the motions of Earth within the solar system and of our solar system within the Milky Way Galaxy, our galaxy is also moving relative to other galaxies in the universe. For nearby galaxies, these motions are somewhat random. For example, our Milky Way Galaxy is moving toward the Andromeda Galaxy. But on larger scales, scientists have discovered that the entire universe is expanding, causing all groupings of galaxies to move away from one another over time.
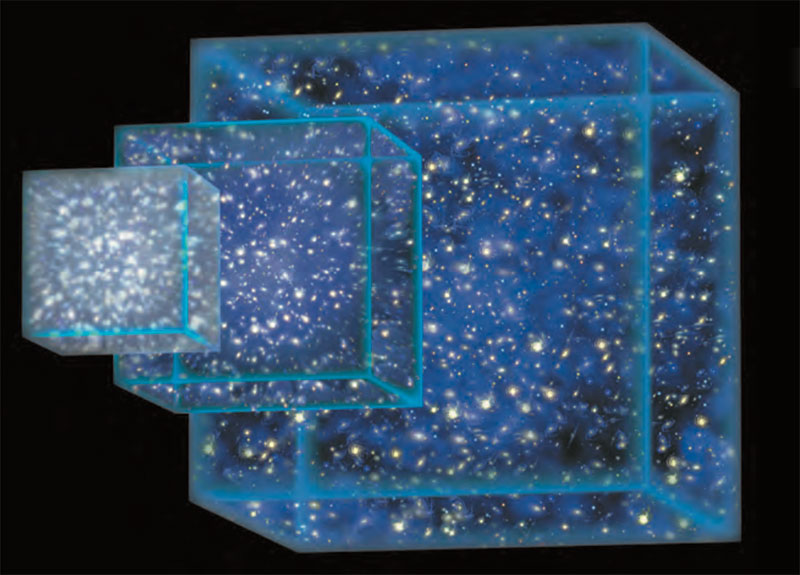
Note that expansion only affects the spacing of galaxies. Individual galaxies— and objects within them such as planets and stars — do not grow larger with time. Scientists therefore say that space itself is expanding, driving apart any galaxies that are not held together by their mutual gravity.
Wow Factor
Expansion, Einstein, Black Holes, and More
The fact that we live in an expanding universe will help you understand many other ideas in modern science. For example, because expansion means galaxies are growing farther apart with time, it implies that galaxies must have been closer together in the past. If we go back far enough, there must be a point at which the expansion began. By measuring the rate of the expansion, scientists have discovered that this beginning must have occurred about 14 billion years ago. Scientists have given this beginning a name: the Big Bang. Notice that the Big Bang was not really an explosion, it is just the name that we give to the beginning of the expansion of the universe.
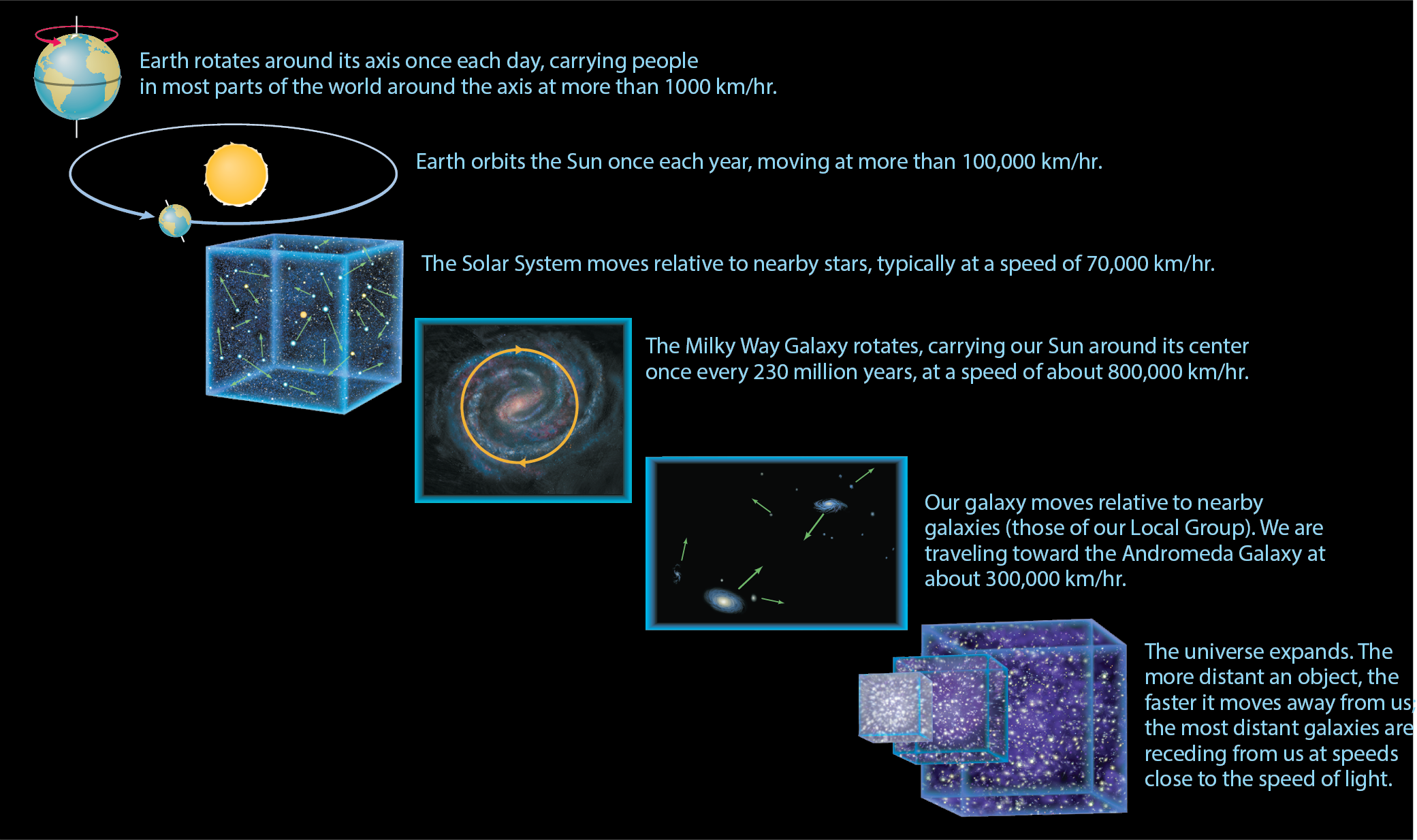
Figure 1.31 summarizes the motions we have discussed in this chapter.
Journal Entry
Perspective on the Universe
Look back at the photo that opens Chapter 1, called the Hubble Extreme Deep Field. By now, you should understand that this photo shows thousands of individual galaxies, each containing billions of stars and planetary systems. Write a paragraph or two describing how what you now know about the universe differs from what you knew before you started this course, and how your new understanding has changed your perspective on our place in the universe.
How do we know?
The Universe is Expanding
The idea of an expanding universe comes from observations first made in the 1920s by the astronomer Edwin Hubble. Using what was then the world’s largest telescope (located on Mt. Wilson in Los Angeles), Hubble developed techniques for estimating the distances of galaxies. In addition, he was able to use something called the Doppler effect (which was already known) to measure the speeds at which galaxies are moving. (You may have heard of the Doppler effect before, because it has many other uses; for example, it is used to measure the motions of storms, police sometimes use it to catch speeders, and it also affects how we hear sounds from moving vehicles.)
As he collected data about the speeds and distances of many galaxies, Hubble discovered two astonishing facts:
- Except for very nearby galaxies, all galaxies in the universe are moving away from us.
- More distant galaxies move away from us at higher speeds.
While these two facts might at first make it sound like we suffer from a cosmic case of chicken pox, there is a much more natural explanation: The entire universe is expanding. You can understand the basic idea by thinking about a raisin cake baking in an oven.
The following video illustrates the analogy. Watch the video, noticing that the cake represents a part of the universe, and the raisins represent galaxies.
As the video shows, an observer living on any particular raisin inside the expanding cake would see all the other raisins moving away, with more distant raisins moving faster. This is exactly what Hubble observed for galaxies in the universe, and today scientists have made many more observations confirming the same ideas. The obvious conclusion is that, much like the cake, our universe is expanding with time. Credit: The Cosmic Perspective.